- Introduction
- MEMON/80 (Martin Eberhard)
- GWMON80 (Jonathan Chapman)
- MON85, HDM80, MONITOR (Dave Dunfield)
- Vector Graphic Monitor 4.0C (mod. by Mike Douglas)
- References
Introduction
Whether IBM PC, Kaypro, NorthStar Horizon, IMSAI 8080 or SOL-20, you will always have to deal with the subject of BIOS, ROM-BIOS and ROM Monitor. Below are a few ROM monitors that I use in my S-100 systems.
MEMON/80
By Martin Eberhard (co-founder of Tesla Motors).
Next some excerpts from MEMON80.ASM supplemented by some important information for the Compupro Interfacer1 by me. I use an Interfacer1 in my IMSAI 8080 as a (direct) replacement for the IMSAI SIO-2.
;==============================================================
; Simple, configurable 1K-byte or 2K-byte ROM-based monitor for
; an 8080- or Z80-based system, supporting a variety of serial
; ports and floppy disk controllers.
;==============================================================
FACTORY settings: IMPORTANT!
"As shipped, both channels A and B will have the DATA port
residing at the port address, and the STATUS port residing
at the port address + 1."
USER settings: just the other way round for MEMON/80!
"If desired, this board may be jumpered so that both channels
have their STATUS ports at the selected address and the DATA
ports at the selected address + 1. This may be accomplished
by cutting the trace between points "B" and "C" at J14 (on
the solder side of the board) and installing a jumper between
points "A" and "B"."
=> CSTAT = CBASE = 00h => port A
=> CDATA = CBASE+1 = 01h
=> TSTAT = TBASE = 02h => port B
=> TDATA = TBASE+1 = 03h
---------------------------------------------------------
CIFAC equ TRUE ;Compupro Interfacer 1 (Port A or B)
TIFAC equ TRUE ;Compupro Interfacer 1 (Port A or B)
; Compupro Interfacer 1 Port A 00h 00h-03h ***
; Port B 02h
;
CBASE equ 000h ;Console Port base address
TBASE equ 002h ;Transfer Port base address
;============================================---------------
;= 3. Specify Memon/80's Memory Utilization =
;============================================
;These specify where Memon/80 is place in memory and where
;its buffers, stack, and variables are. Additionally, you
;can disable some Memon/80 features to reduce the code size.
;-----------------------------------------------------------
;MEBASE equ 0F800h ;Base address of Memon/80 code
MEBASE equ 0C000h ;same as on my N*
;--------------------------------------------------------
;Compupro Interfacer 1 Equates
;
;The Interfacer 1 is built around a pair of 1602-type
;generic UARTs, with jumper selectable baud rate
;generators and with external logic providing status
;and control registers.
;
;Control bits are configured with jumpers. the board will
;XOR whatever you write to the control port with the
;jumper setting. This assumes all jumpers are set to 0.
;--------------------------------------------------------
if CIFAC
CSTAT equ CBASE ;Console STATUS
CCTRL equ CBASE ;Console control
CDATA equ CBASE+1 ;Console DATA
CTXRDY equ 01h ;channel a Tx ready bit
CRXRDY equ 02h ;channel a Rx ready bit
endif ;CIFAC
if TIFAC
TPORT set TRUE ;Transfer port is defined
TSTAT equ TBASE ;Transfer Port status
TCTRL equ TBASE ;Transfer Port control
TDATA equ TBASE+1 ;Transfer Port data
TTXRDY equ 01h ;channel B Tx ready bit
TRXRDY equ 02h ;channel B Rx ready bit
endif ;TIFAC
if CIFAC or TIFAC
IFRST equ 0ACH ;reset: 8 data, no parity, flow
;..control outputs high, no ints
endif ;CIFAC or TIFAC
;--------------------------------------------
;Initialize both Compupro Interfacer channels
;--------------------------------------------
if CIFAC or TIFAC
mvi a,IFRST
endif ;CIFAC or TIFAC
if CIFAC
out CCTRL
endif ;CIFAC
if TIFAC
out TCTRL
endif ;TIFAC
MEMON/80 expects the STATUS address first and then the DATA address for both the console port and the transfer port!
Port A:
CSTAT = CBASE = 00h
CDATA = CBASE+1 = 01h
Port B:
TSTAT = TBASE = 02h
TDATA = TBASE+1 = 03h
But the Interfacer1 is very flexible. You can change the ports and the address order. I did so for my IMSAI 8080. Here the Interfacer1 is a direct replacement for the IMSAI SIO-2. Works fine!
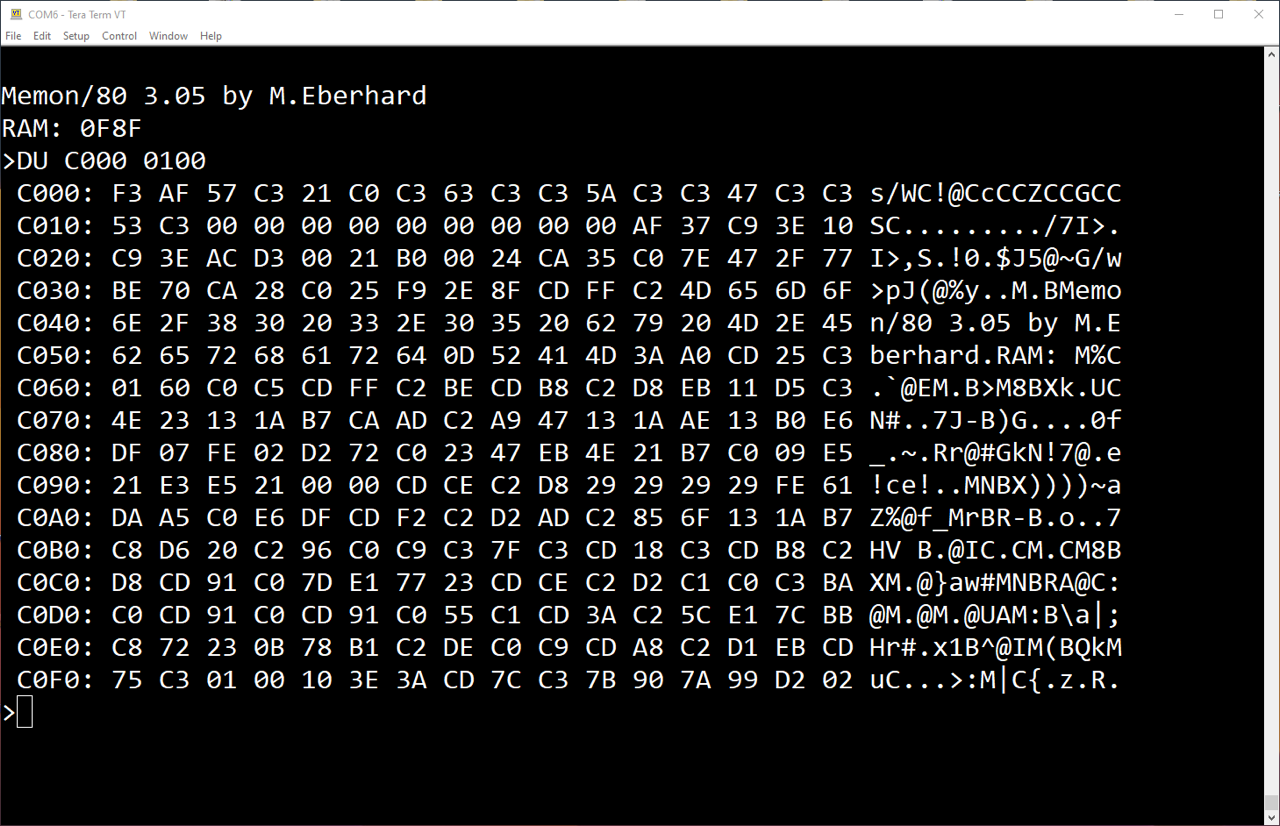
(on my IMSAI 8080 with RAM-4K)
Commands
;==============================================================
;Memon/80 Commands (all values are in HEX)
;
; BO <DRIVE> {Some controllers require ROM2K}
; Boot from floppy disk. The <DRIVE> option ( a number
; between 0 and 3) is only available for the Cromemco disk
; controllers, because CDOS is one of the few S100 operating
; systems that allows booting from anything but the first
; drive.
;
; CE [command line] {Requires ROM2K}
; Execute CP/M program: Copy Command line (any text string)
; to RAM at 0080h, install WBOOT jump at 0000h, and jump to
; program at 0100h.
;
; CO <SRC> <DST> <BCNT> [<RPT>]
; Copy <BCNT> bytes of memory from address <SRC> to address
; <DST>. The <RPT> option is available only if CORPT=TRUE.
; This optionally repeats the copy <RPT> times. (This is for
; programming EPROMS with e.g. a Cromemco bytesaver).
;
; DU [<ADR> [<BCNT>]]
; Dump <BCNT> (which defaults to 1) bytes of memory in both
; hex and ASCII, starting at address <ADR> (defaults to 0).
;
; EN [<ADR>]
; Enter hex data into memory at <ADR>, which defaults to 0.
; values are separated with spaces or CR'S. Quit EN command
; with a blank line.
;
; EX [[<ADR>] <OPT>]
; Execute at <ADR>, which defaults to 0. ProgramS can RET
; to Memon/80'S main loop.
; <OPT> is available only of ROM2K=TRUE. If <OPT>=1 then
; Memon/80 executes an IN from port FFh before jumping to
; the specified address. (This disables PROM on the
; MITS 8800b Turnkey Module and on my 88-2SIOJP.)
;
; FI [<ADR> [<BCNT> [<VAL>]]]
; Fill <BCNT> bytes of memory starting at <ADR> with <VAL>,
; <VAL> and <ADR> default to 0. <BCNT> defaults to all RAM.
; Stop when fill reaches Memon/80'S RAM page.
;
; HD <ADR> <BCNT>
; Intel hex dump <BCNT> bytes of memory starting at <ADR>,
; to the Transfer Port
;
; HL [<OFST>]
; Load Intel hex file to memory from the Transfer Port. Add
; optional address offset <OFST> to each record address.
; This will generate a "Mem" error if a record will write
; over Memon/80's RAM page (or RAM image, if RAMCOD=TRUE).
; HL will report the total number of records received when
; an Intel hex EOF record is received, if ROM2K=TRUE.
;
; IN <PORT>
; Input from <PORT> and print result on Console
;
; MT <ADR> <CNT> {Requires ROM2K}
; Test <CNT> bytes of memory, starting at <ADR>. This is a
; destructive test - RAM will be filled with garbage. Errors
; are reported to the Console. This will skip over the
; portion of RAM that Memon uses for its stack.
;
; OT <PORT> <data>
; Output <data> to <PORT>
;
; SE <ADR> <Byte1> [<byte2> [<byte3> [..<Byten>]]]
; or
; SE <ADR> 'text string' {Requires ROM2K}
; Search for string in memory, starting at address <ADR>
; Can also mix forms e.g.
; SE 100 'Hello world' 0D 0A 'second line'
;
; TB <BAUD> {Requires ROM2K}
; {deleted if no Transfer Port specified}
; Set TRansfer Port baud rate, <BAUD> from this table:
; Value Baud Rate
; 0 110 (2 stop bits)
; 1 150
; 2 300
; 3 600
; 4 1200
; 5 2400
; 6 4800
; 7 9600
; 8 19200
; 9 38400
; A 76800
;
; This command is only available if the serial port board
; that's selected to be the Transfer Port allows software to
; set its baud rate. Not all baud rates are available for
; every board. Attempting to select an unsupported baud rate
; will result in a command error.
;
; TE [<EXCHR>] {deleted if no Transfer Port specified}
; Terminal mode: Console keyboard input goes to Port B
; output, and Port B input goes to the Console output.
; Type CTRL-<EXCHR> (which defaults to CTRL-C) to exit.
;
; TP [<0/1>] {deleted if no Transfer Port specified}
; Enable the Transfer Port. "TP 0" disables the Transfer
; port, causing Transfer Port operations to use the Console
; Port instead. defaults to 1 (enabled).
;
; VE <SRC> <DST> <BCNT>
; Verify <BCNT> bytes of memory, starting at <SRC> and <DST>
;==============================================================
HEX Load (HL)
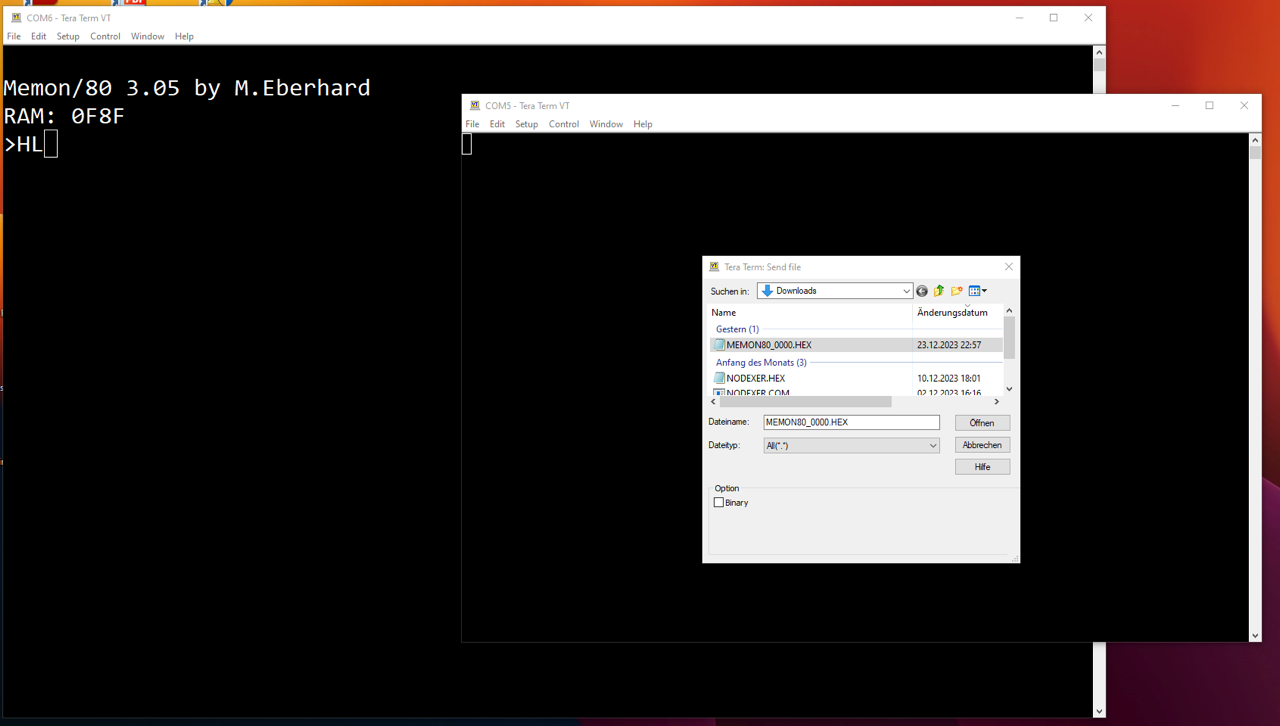
I simply loaded MEMON/80 starting from memory location 0000h. Of course you have to adapt the HEX file for this.
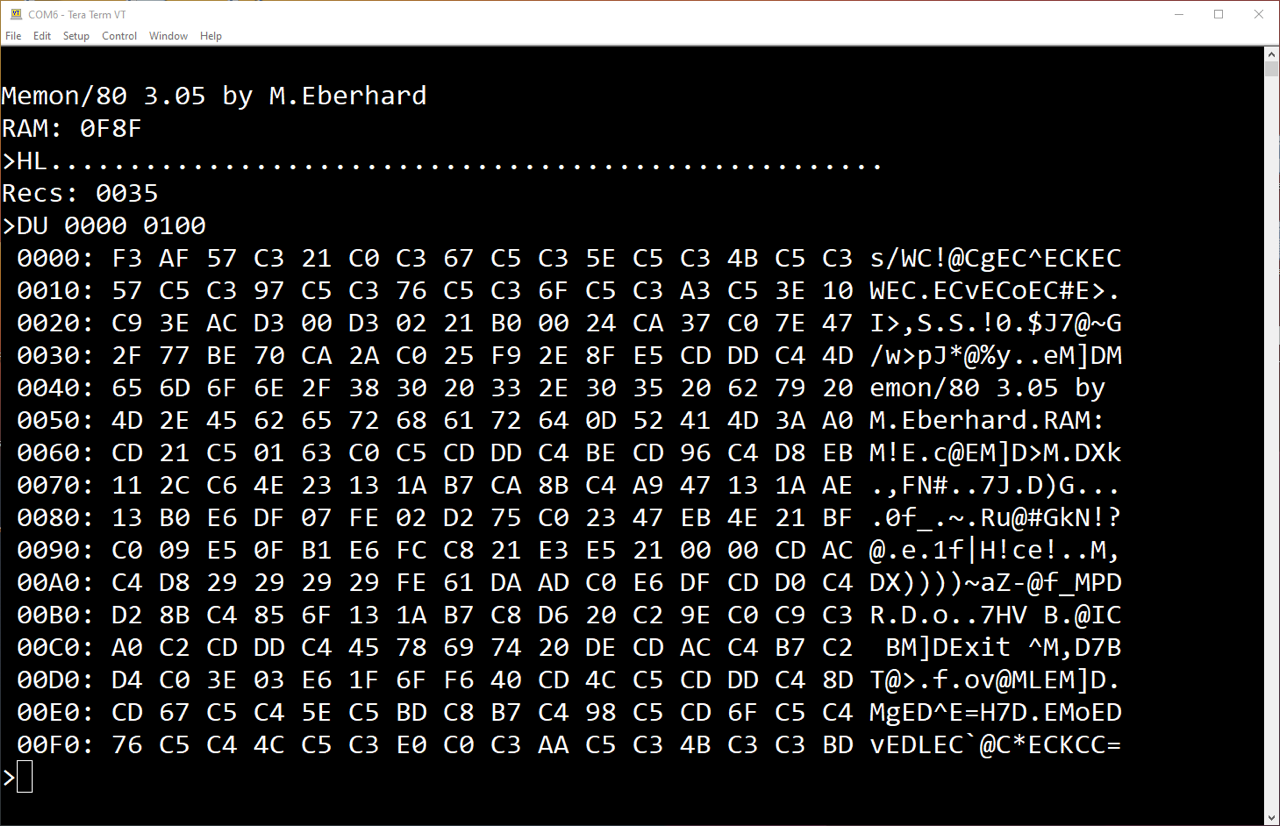
GWMON80
By Jonathan Chapman (The Glitch Works).
GWMON-80 is intended to be a simple ROM-type system monitor for systems utilizing processors that are binary-compatible with the 8080, including (but not limited to) 8085 and Z80 systems. It is written in a modular format so that it can be extended for use with specific system hardware with ease. [1]
The following customizations are available and can be built using `make`
and the contents of the `Make Target` column.
| Make Target | SM | XM | Description |
|-------------|:--:|:--:|----------------------------------------------------|
| `8085r1` | Y | N | Glitch Works 8085 SBC rev 1, 8085 bit-bang serial |
| `8085r3` | Y | N | Glitch Works 8085 SBC rev 3 |
| `certek2` | Y | N | Certek SBC85-2, 8085 bit-bang serial |
| `cpm80` | Y | N | CP/M-80 1.4 through 3.0, primarily for development |
| `cscc` | Y | N | Cromemco SCC (Single Card Computer) |
| `imsai1` | Y | N | IMSAI SIO2 and compatible (usually S-100) |
| `mits1` | Y | N | MITS 88-2SIO and compatible (usually S-100) |
| `mits2` | Y | N | MITS 88-SIO rev 1 and compatible (usually S-100) |
| `mits3` | Y | N | MITS Turnkey board (usually S-100) |
| `sds100` | Y | N | SD Systems SBC-100 |
| `sds200` | Y | N | SD Systems SBC-200 |
| `tdlsmb` | Y | N | Technical Design Labs SMB, TTY ACIA |
| `vgzcb` | Y | N | Vector Graphic ZCB with default USART addressing |
[1]
I use the imsai1 configuration; works fine with my Interfacer1.

Commands
The Small Monitor (SM) command syntax is as follows:
D XXXX YYYY Dump memory from XXXX to YYYY
E XXXX Edit memory starting at XXXX (CTRL+C to end)
G XXXX GO starting at address XXXX
I XX Input from I/O port XX and display as hex
O XX YY Output to I/O port XX byte YY
L Load an Intel HEX file into memory
Summary
GWMON80 is a very minimalistic monitor but it fits on an 2704 (512) EPROM. But the most important commands such as DUMP, (HEX)LOAD and GO are available. Unfortunately, there is no COPY command to copy bytes from one area to another.
References
- (↑) Jonathan Chapman, GWMON80, README.MD